Redis(七):set/sadd/sismember/sinter/sdiffstore 命令源码解析
上两篇我们讲了hash和list数据类型相关的主要实现方法,同时加上前面对框架服务和string相关的功能介绍,已揭开了大部分redis的实用面纱。
现在还剩下两种数据类型: set, zset.
本篇咱们继续来看redis中的数据类型的实现: set 相关操作实现。
研究过jdk的hashmap和hashset实现的同学,肯定都是知道,set其实就是一个简化版的map,只要将map的 k->v 的形式变为 k->1 的形式就可以了。所以set只是map的一个简单包装类。
同理,对于 redis的 hash 和 set 数据类型,我们是否可以得出这么个结论呢?(如果是那样的话,我们就只需看几个set提供的特殊功能即可)
同样,我们从功能列表开始,到数据结构,再到具体实现的这么个思路,来探索redis set的实现吧。
零、redis set相关操作方法
Redis 的 Set 是 String 类型的无序集合。集合成员是唯一的,这就意味着集合中不能出现重复的数据。可根据应用场景需要选用该数据类型。(比如:好友/关注/粉丝/感兴趣的人/黑白名单)
从官方的手册中可以查到相关的使用方法。
1> SADD key member1 [member2]
功能: 向集合添加一个或多个成员
返回值: 本次添加到redis的member数量(不包含已存在的member)2> SCARD key
功能: 获取集合的成员数
返回值: set的元素数量或者03> SDIFF key1 [key2]
功能: 返回给定所有集合的差集
返回值: 差集的数组列表4> SDIFFSTORE destination key1 [key2]
功能: 返回给定所有集合的差集并存储在 destination 中
返回值: 差集元素个数5> SINTER key1 [key2]
功能: 返回给定所有集合的交集
返回值: 交集的数组列表6> SINTERSTORE destination key1 [key2]
功能: 返回给定所有集合的交集并存储在 destination 中
返回值: 交集的元素个数7> SISMEMBER key member
功能: 判断 member 元素是否是集合 key 的成员
返回值: 1:如果member是key的成员, 0:如果member不是key的成员或者key不存在8> SMEMBERS key
功能: 返回集合中的所有成员
返回值: 所有成员列表9> SMOVE source destination member
功能: 将 member 元素从 source 集合移动到 destination 集合
返回值: 1:移动操作成功, 0:移动不成功(member不是source的成员)10> SPOP key [count]
功能: 移除并返回集合中的一个随机元素(因为set是无序的)
返回值: 被移除的元素列表或者nil11> SRANDMEMBER key [count]
功能: 返回集合中一个或多个随机数
返回值: 1个元素或者count个元素数组列表或者nil12> SREM key member1 [member2]
功能: 移除集合中一个或多个成员
返回值: 实际移除的元素个数13> SUNION key1 [key2]
功能: 返回所有给定集合的并集
返回值: 并集元素数组列表14> SUNIONSTORE destination key1 [key2]
功能: 所有给定集合的并集存储在 destination 集合中
返回值: 并集元素个数15> SSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
功能: 迭代集合中的元素
返回值: 元素数组列表
一、set 相关数据结构
redis使用dict和intset 两种数据结构保存set数据。
// 1. inset 数据结构,在set数据量小且都是整型数据时使用typedef struct intset {// 编码范围,由具体存储值决定uint32_t encoding;// 数组长度uint32_t length;// 具体存储元素的容器int8_t contents[];} intset;// 2. dict 相关数据结构,即是 hash 的实现相关的数据结构/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */typedef struct dictht {dictEntry **table;unsigned long size;unsigned long sizemask;unsigned long used;} dictht;typedef struct dict {dictType *type;void *privdata;dictht ht[2];long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */} dict;/* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call* dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while* iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext()* should be called while iterating. */typedef struct dictIterator {dict *d;long index;int table, safe;dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry;/* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */long long fingerprint;} dictIterator;typedef struct dictEntry {void *key;union {void *val;uint64_t u64;int64_t s64;double d;} v;struct dictEntry *next;} dictEntry;typedef struct dictType {unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);} dictType;
对于set相关的命令的接口定义:
{"sadd",saddCommand,-3,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"srem",sremCommand,-3,"wF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"smove",smoveCommand,4,"wF",0,NULL,1,2,1,0,0},{"sismember",sismemberCommand,3,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"scard",scardCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"spop",spopCommand,-2,"wRsF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"srandmember",srandmemberCommand,-2,"rR",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"sinter",sinterCommand,-2,"rS",0,NULL,1,-1,1,0,0},{"sinterstore",sinterstoreCommand,-3,"wm",0,NULL,1,-1,1,0,0},{"sunion",sunionCommand,-2,"rS",0,NULL,1,-1,1,0,0},{"sunionstore",sunionstoreCommand,-3,"wm",0,NULL,1,-1,1,0,0},{"sdiff",sdiffCommand,-2,"rS",0,NULL,1,-1,1,0,0},{"sdiffstore",sdiffstoreCommand,-3,"wm",0,NULL,1,-1,1,0,0},{"smembers",sinterCommand,2,"rS",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},{"sscan",sscanCommand,-3,"rR",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
二、sadd 添加成员操作
一般我们都会以添加数据开始。从而理解数据结构的应用。
// 用法: SADD key member1 [member2]// t_set.c, 添加membervoid saddCommand(client *c) {robj *set;int j, added = 0;// 先从当前db中查找set实例set = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]);if (set == NULL) {// 1. 新建set实例并添加到当前db中set = setTypeCreate(c->argv[2]->ptr);dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[1],set);} else {if (set->type != OBJ_SET) {addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);return;}}// 对于n个member,一个个地添加即可for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) {// 2. 只有添加成功, added 才会加1if (setTypeAdd(set,c->argv[j]->ptr)) added++;}// 命令传播if (added) {signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,"sadd",c->argv[1],c->db->id);}server.dirty += added;// 响应添加成功的数量addReplyLongLong(c,added);}// 1. 创建新的set集合实例(需根据首次的参数类型判定)// t_set.c, 创建set实例/* Factory method to return a set that *can* hold "value". When the object has* an integer-encodable value, an intset will be returned. Otherwise a regular* hash table. */robj *setTypeCreate(sds value) {// 如果传入的value是整型,则创建 intset 类型的set// 否则使用dict类型的set// 一般地,第一个数据为整型,后续数据也应该为整型,所以这个数据结构相对稳定// 而hash的容器创建时,只使用了一 ziplist 创建,这是不一样的实现if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,NULL) == C_OK)return createIntsetObject();return createSetObject();}// 1.1. 创建 intset 型的set// object.crobj *createIntsetObject(void) {intset *is = intsetNew();robj *o = createObject(OBJ_SET,is);o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET;return o;}// intset.c, new一个空的intset对象/* Create an empty intset. */intset *intsetNew(void) {intset *is = zmalloc(sizeof(intset));is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(INTSET_ENC_INT16);is->length = 0;return is;}// 1.2. 创建dict 型的setrobj *createSetObject(void) {dict *d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);robj *o = createObject(OBJ_SET,d);o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;return o;}// dict.c/* Create a new hash table */dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,void *privDataPtr){dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d));_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);return d;}/* Initialize the hash table */int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,void *privDataPtr){_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);d->type = type;d->privdata = privDataPtr;d->rehashidx = -1;d->iterators = 0;return DICT_OK;}// 2. 添加member到set集合中// t_set.c, 添加元素/* Add the specified value into a set.** If the value was already member of the set, nothing is done and 0 is* returned, otherwise the new element is added and 1 is returned. */int setTypeAdd(robj *subject, sds value) {long long llval;// 2.1. HT编码和INTSET编码分别处理就好if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {dict *ht = subject->ptr;// 以 value 为 key, 添加实例到ht中// 实现过程也很简单,大概就是如果存在则返回NULL(即无需添加),辅助rehash,分配内存创建dictEntry实例,稍后简单看看dictEntry *de = dictAddRaw(ht,value);if (de) {// 重新设置key为 sdsdup(value), value为NULLdictSetKey(ht,de,sdsdup(value));dictSetVal(ht,de,NULL);return 1;}}// 2.2. intset 编码的member添加else if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {// 尝试解析value为 long 型,值写入 llval 中if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == C_OK) {uint8_t success = 0;// 情况1. 可添加到intset中subject->ptr = intsetAdd(subject->ptr,llval,&success);if (success) {/* Convert to regular set when the intset contains* too many entries. */// 默认: 512, intset大于之后,则转换为ht hash表模式存储if (intsetLen(subject->ptr) > server.set_max_intset_entries)// 2.3. 转换intset编码为 ht 编码setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);return 1;}} else {// 情况2. member 是字符串型,先将set容器转换为 ht 编码,再重新执行dict的添加模式/* Failed to get integer from object, convert to regular set. */setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);/* The set *was* an intset and this value is not integer* encodable, so dictAdd should always work. */serverAssert(dictAdd(subject->ptr,sdsdup(value),NULL) == DICT_OK);return 1;}} else {serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");}return 0;}// 2.1. 添加member到dict中(略解, 在hash数据结构解析中已介绍)// dict.c, 添加某key到 d 字典中/* Low level add. This function adds the entry but instead of setting* a value returns the dictEntry structure to the user, that will make* sure to fill the value field as he wishes.** This function is also directly exposed to the user API to be called* mainly in order to store non-pointers inside the hash value, example:** entry = dictAddRaw(dict,mykey);* if (entry != NULL) dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry,1000);** Return values:** If key already exists NULL is returned.* If key was added, the hash entry is returned to be manipulated by the caller.*/dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key){int index;dictEntry *entry;dictht *ht;if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if* the element already exists. */// 获取需要添加的key的存放位置下标(slot), 如果该key已存在, 则返回-1(无可用slot)if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1)return NULL;/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry.* Insert the element in top, with the assumption that in a database* system it is more likely that recently added entries are accessed* more frequently. */ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));entry->next = ht->table[index];ht->table[index] = entry;ht->used++;/* Set the hash entry fields. */dictSetKey(d, entry, key);return entry;}// 2.2. 添加整型数据到 intset中// intset.c, 添加value/* Insert an integer in the intset */intset *intsetAdd(intset *is, int64_t value, uint8_t *success) {// 获取value的所属范围uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);uint32_t pos;if (success) *success = 1;/* Upgrade encoding if necessary. If we need to upgrade, we know that* this value should be either appended (if > 0) or prepended (if < 0),* because it lies outside the range of existing values. */// 默认 is->encoding 为 INTSET_ENC_INT16 (16位长)// 2.2.1. 即超过当前预设的位长,则需要增大预设,然后添加// 此时的value可以确定: 要么是最大,要么是最小 (所以我们可以推断,此intset应该是有序的)if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding)) {/* This always succeeds, so we don't need to curry *success. */return intsetUpgradeAndAdd(is,value);} else {/* Abort if the value is already present in the set.* This call will populate "pos" with the right position to insert* the value when it cannot be found. */// 2.2.2. 在当前环境下添加value// 找到value则说明元素已存在,不可再添加// pos 保存比value小的第1个元素的位置if (intsetSearch(is,value,&pos)) {if (success) *success = 0;return is;}is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);// 在pos不是末尾位置时,需要留出空位,依次移动后面的元素if (pos < intrev32ifbe(is->length)) intsetMoveTail(is,pos,pos+1);}// 针对编码位不变更的情况下设置pos位置的值_intsetSet(is,pos,value);is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);return is;}// 判断 value 的位长// INTSET_ENC_INT16 < INTSET_ENC_INT32 < INTSET_ENC_INT64// 2 < 4 < 8/* Return the required encoding for the provided value. */static uint8_t _intsetValueEncoding(int64_t v) {if (v < INT32_MIN || v > INT32_MAX)return INTSET_ENC_INT64;else if (v < INT16_MIN || v > INT16_MAX)return INTSET_ENC_INT32;elsereturn INTSET_ENC_INT16;}// 2.2.1. 升级预设位长,并添加value// intset.c/* Upgrades the intset to a larger encoding and inserts the given integer. */static intset *intsetUpgradeAndAdd(intset *is, int64_t value) {uint8_t curenc = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);uint8_t newenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);int length = intrev32ifbe(is->length);int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0;/* First set new encoding and resize */is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(newenc);// 每次必进行扩容is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);/* Upgrade back-to-front so we don't overwrite values.* Note that the "prepend" variable is used to make sure we have an empty* space at either the beginning or the end of the intset. */// 因编码发生变化,元素的位置已经不能一一对应,需要按照原来的编码依次转移过来// 从后往前依次赋值,所以,内存位置上不存在覆盖问题(后面内存位置一定是空的),直接依次赋值即可(高效复制)while(length--)_intsetSet(is,length+prepend,_intsetGetEncoded(is,length,curenc));/* Set the value at the beginning or the end. */// 对新增加的元素,负数添加到第0位,否则添加到最后一个元素后一位if (prepend)_intsetSet(is,0,value);else_intsetSet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length),value);is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);return is;}/* Resize the intset */static intset *intsetResize(intset *is, uint32_t len) {uint32_t size = len*intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);// mallocis = zrealloc(is,sizeof(intset)+size);return is;}// intset.c, 获取pos位置的值/* Return the value at pos, given an encoding. */static int64_t _intsetGetEncoded(intset *is, int pos, uint8_t enc) {int64_t v64;int32_t v32;int16_t v16;if (enc == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {memcpy(&v64,((int64_t*)is->contents)+pos,sizeof(v64));memrev64ifbe(&v64);return v64;} else if (enc == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {memcpy(&v32,((int32_t*)is->contents)+pos,sizeof(v32));memrev32ifbe(&v32);return v32;} else {memcpy(&v16,((int16_t*)is->contents)+pos,sizeof(v16));memrev16ifbe(&v16);return v16;}}// intset.c, 设置pos位置的值,和数组赋值的实际意义差不多// 只是这里数据类型是不确定的,所以使用指针进行赋值/* Set the value at pos, using the configured encoding. */static void _intsetSet(intset *is, int pos, int64_t value) {uint32_t encoding = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {((int64_t*)is->contents)[pos] = value;memrev64ifbe(((int64_t*)is->contents)+pos);} else if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {((int32_t*)is->contents)[pos] = value;memrev32ifbe(((int32_t*)is->contents)+pos);} else {((int16_t*)is->contents)[pos] = value;memrev16ifbe(((int16_t*)is->contents)+pos);}}// 2.2.2. 在编码类型未变更的情况,需要查找可以存放value的位置(为了确认该value是否已存在,以及小于value的第一个位置赋值)/* Search for the position of "value". Return 1 when the value was found and* sets "pos" to the position of the value within the intset. Return 0 when* the value is not present in the intset and sets "pos" to the position* where "value" can be inserted. */static uint8_t intsetSearch(intset *is, int64_t value, uint32_t *pos) {int min = 0, max = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1, mid = -1;int64_t cur = -1;/* The value can never be found when the set is empty */if (intrev32ifbe(is->length) == 0) {if (pos) *pos = 0;return 0;} else {/* Check for the case where we know we cannot find the value,* but do know the insert position. */// 因 intset 是有序数组,即可以判定是否超出范围,如果超出则元素必定不存在if (value > _intsetGet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1)) {if (pos) *pos = intrev32ifbe(is->length);return 0;} else if (value < _intsetGet(is,0)) {if (pos) *pos = 0;return 0;}}// 使用二分查找while(max >= min) {mid = ((unsigned int)min + (unsigned int)max) >> 1;cur = _intsetGet(is,mid);if (value > cur) {min = mid+1;} else if (value < cur) {max = mid-1;} else {// 找到了break;}}if (value == cur) {if (pos) *pos = mid;return 1;} else {// 在没有找到的情况下,min就是第一个比 value 小的元素if (pos) *pos = min;return 0;}}// intset移动(内存移动)static void intsetMoveTail(intset *is, uint32_t from, uint32_t to) {void *src, *dst;uint32_t bytes = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-from;uint32_t encoding = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {src = (int64_t*)is->contents+from;dst = (int64_t*)is->contents+to;bytes *= sizeof(int64_t);} else if (encoding == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {src = (int32_t*)is->contents+from;dst = (int32_t*)is->contents+to;bytes *= sizeof(int32_t);} else {src = (int16_t*)is->contents+from;dst = (int16_t*)is->contents+to;bytes *= sizeof(int16_t);}memmove(dst,src,bytes);}// 2.3. 转换intset编码为 ht 编码 (如果遇到string型的value或者intset数量大于阀值(默认:512)时)// t_set.c, 类型转换/* Convert the set to specified encoding. The resulting dict (when converting* to a hash table) is presized to hold the number of elements in the original* set. */void setTypeConvert(robj *setobj, int enc) {setTypeIterator *si;// 要求外部必须保证 set类型且 intset 编码serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,setobj,setobj->type == OBJ_SET &&setobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET);if (enc == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {int64_t intele;// 直接创建一个 dict 来容纳数据dict *d = dictCreate(&setDictType,NULL);sds element;/* Presize the dict to avoid rehashing */// 直接一次性扩容成需要的大小dictExpand(d,intsetLen(setobj->ptr));/* To add the elements we extract integers and create redis objects */// setTypeIterator 迭代器是转换的关键si = setTypeInitIterator(setobj);while (setTypeNext(si,&element,&intele) != -1) {// element:ht编码时的key, intele: intset编码时的valueelement = sdsfromlonglong(intele);// 因set特性保证是无重复元素,所以添加dict时,必然应成功// 此处应无 rehash, 而是直接计算 hashCode, 放置元素, 时间复杂度 O(1)serverAssert(dictAdd(d,element,NULL) == DICT_OK);}// 释放迭代器setTypeReleaseIterator(si);setobj->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_HT;zfree(setobj->ptr);setobj->ptr = d;} else {serverPanic("Unsupported set conversion");}}// t_set.c, 获取set集合的迭代器setTypeIterator *setTypeInitIterator(robj *subject) {setTypeIterator *si = zmalloc(sizeof(setTypeIterator));// 设置迭代器公用信息si->subject = subject;si->encoding = subject->encoding;// hash表则需要再迭代 dictif (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {si->di = dictGetIterator(subject->ptr);}// intset 比较简单,直接设置下标即可else if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {si->ii = 0;} else {serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");}return si;}// dict.c, dict迭代器初始化dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d){dictIterator *iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter));iter->d = d;iter->table = 0;iter->index = -1;iter->safe = 0;iter->entry = NULL;iter->nextEntry = NULL;return iter;}// t_set.c,/* Move to the next entry in the set. Returns the object at the current* position.** Since set elements can be internally be stored as SDS strings or* simple arrays of integers, setTypeNext returns the encoding of the* set object you are iterating, and will populate the appropriate pointer* (sdsele) or (llele) accordingly.** Note that both the sdsele and llele pointers should be passed and cannot* be NULL since the function will try to defensively populate the non* used field with values which are easy to trap if misused.** When there are no longer elements -1 is returned. */int setTypeNext(setTypeIterator *si, sds *sdsele, int64_t *llele) {// hash表返回keyif (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {dictEntry *de = dictNext(si->di);if (de == NULL) return -1;*sdsele = dictGetKey(de);*llele = -123456789; /* Not needed. Defensive. */}// intset 直接获取下标对应的元素即可else if (si->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {if (!intsetGet(si->subject->ptr,si->ii++,llele))return -1;*sdsele = NULL; /* Not needed. Defensive. */} else {serverPanic("Wrong set encoding in setTypeNext");}return si->encoding;}// case1: intset直接叠加下标即可// intset.c/* Sets the value to the value at the given position. When this position is* out of range the function returns 0, when in range it returns 1. */uint8_t intsetGet(intset *is, uint32_t pos, int64_t *value) {if (pos < intrev32ifbe(is->length)) {*value = _intsetGet(is,pos);return 1;}return 0;}/* Return the value at pos, using the configured encoding. */static int64_t _intsetGet(intset *is, int pos) {return _intsetGetEncoded(is,pos,intrev32ifbe(is->encoding));}/* Return the value at pos, given an encoding. */static int64_t _intsetGetEncoded(intset *is, int pos, uint8_t enc) {int64_t v64;int32_t v32;int16_t v16;if (enc == INTSET_ENC_INT64) {memcpy(&v64,((int64_t*)is->contents)+pos,sizeof(v64));memrev64ifbe(&v64);return v64;} else if (enc == INTSET_ENC_INT32) {memcpy(&v32,((int32_t*)is->contents)+pos,sizeof(v32));memrev32ifbe(&v32);return v32;} else {memcpy(&v16,((int16_t*)is->contents)+pos,sizeof(v16));memrev16ifbe(&v16);return v16;}}// (附带)case2: dict的迭代// dict.c, dict的迭代,存疑问dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter){// 一直迭代查找while (1) {// iter->entry 为NULL, 有两种可能: 1. 初始化时; 2. 上一元素为迭代完成(hash冲突)if (iter->entry == NULL) {dictht *ht = &iter->d->ht[iter->table];if (iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0) {if (iter->safe)iter->d->iterators++;elseiter->fingerprint = dictFingerprint(iter->d);}// 直接使用下标进行迭代,如果中间有空闲位置该如何处理??// 看起来redis是使用了全量迭代元素的处理办法,即有可能有许多空迭代过程// 一般地,也是进行两层迭代,jdk的hashmap迭代实现为直接找到下一次非空的元素为止iter->index++;// 直到迭代完成所有元素,否则会直到找到一个元素为止if (iter->index >= (long) ht->size) {if (dictIsRehashing(iter->d) && iter->table == 0) {iter->table++;iter->index = 0;ht = &iter->d->ht[1];} else {break;}}iter->entry = ht->table[iter->index];} else {// entry不为空,就一定有nextEntry??iter->entry = iter->nextEntry;}// 如果当前entry为空,则继续迭代下一个 indexif (iter->entry) {/* We need to save the 'next' here, the iterator user* may delete the entry we are returning. */iter->nextEntry = iter->entry->next;return iter->entry;}}return NULL;}
其实sadd过程非常简单。与hash的实现方式只是在 dict 上的操作是一致的,但本质上是不一样的。我们通过一个时序图整体看一下:
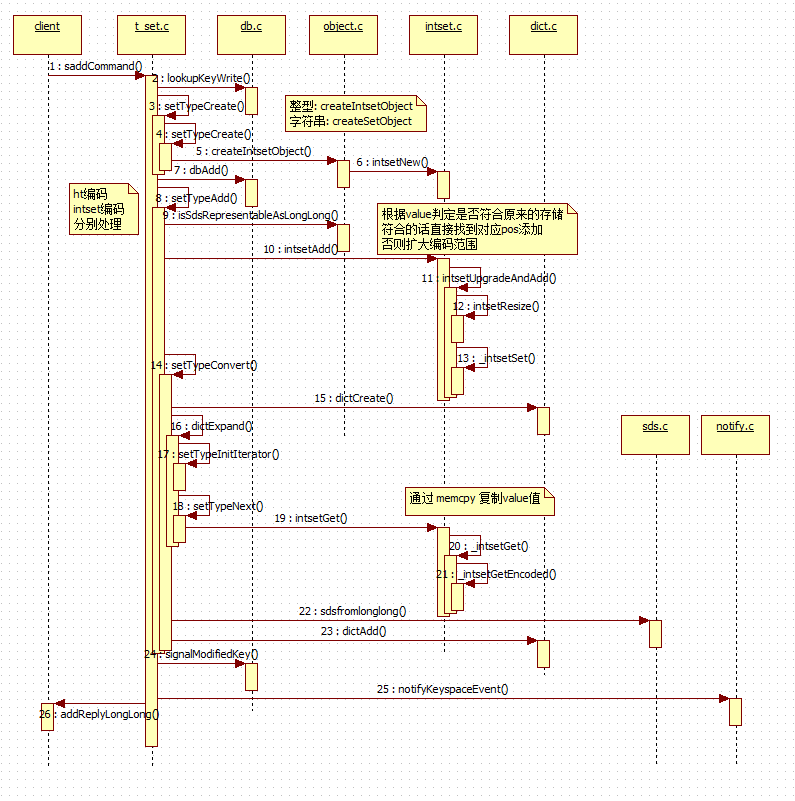
三、sismember 元素查找操作
由于set本身的特性决定,它不会有许多查询功能也没必要提供丰富的查询功用。所以只能先挑这个来看看了。要确定一个元素是不是其成员,无非就是一个比较的过程。
// 用法: SISMEMBER key member// t_set.c,void sismemberCommand(client *c) {robj *set;if ((set = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.czero)) == NULL ||checkType(c,set,OBJ_SET)) return;// 主要方法 setTypeIsMemberif (setTypeIsMember(set,c->argv[2]->ptr))// 回复1addReply(c,shared.cone);else// 回复0addReply(c,shared.czero);}// t_set.cint setTypeIsMember(robj *subject, sds value) {long long llval;if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// hash 表的查找方式,hashCode 计算,链表查找,就这么简单return dictFind((dict*)subject->ptr,value) != NULL;} else if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {// 如果当前的set集合是 intset 编码的,则只有查找值也是整型的情况下才可能查找到元素if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == C_OK) {// intset 查找,而且 intset 是有序的,所以直接使用二分查找即可return intsetFind((intset*)subject->ptr,llval);}} else {serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");}return 0;}/* Determine whether a value belongs to this set */uint8_t intsetFind(intset *is, int64_t value) {uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);// 最大范围检查,加二分查找// intsetSearch 前面已介绍return valenc <= intrev32ifbe(is->encoding) && intsetSearch(is,value,NULL);}
四、sinter 集合交集获取
两个set的数据集取交集,也是要看使用场景吧。(比如获取共同的好友)
在看redis的实现之前,我们可以自己先想想,如何实现两个集合次问题?(算法题)我只能想到无脑地两重迭代加hash的方式。你呢?
// 用法: SINTER key1 [key2]// t_set.c, sinter 实现void sinterCommand(client *c) {// 第三个参数是用来存储 交集结果的,两段代码已做复用,说明存储过程还是比较简单的sinterGenericCommand(c,c->argv+1,c->argc-1,NULL);}// t_set.c, 求n个key的集合交集void sinterGenericCommand(client *c, robj **setkeys,unsigned long setnum, robj *dstkey) {robj **sets = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*setnum);setTypeIterator *si;robj *dstset = NULL;sds elesds;int64_t intobj;void *replylen = NULL;unsigned long j, cardinality = 0;int encoding;for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {// 依次查找每个key的set实例robj *setobj = dstkey ?lookupKeyWrite(c->db,setkeys[j]) :lookupKeyRead(c->db,setkeys[j]);// 只要有一个set为空,则交集必定为为,无需再找if (!setobj) {zfree(sets);if (dstkey) {// 没有交集,直接将dstKey 删除,注意此逻辑??if (dbDelete(c->db,dstkey)) {signalModifiedKey(c->db,dstkey);server.dirty++;}addReply(c,shared.czero);} else {addReply(c,shared.emptymultibulk);}return;}if (checkType(c,setobj,OBJ_SET)) {zfree(sets);return;}sets[j] = setobj;}/* Sort sets from the smallest to largest, this will improve our* algorithm's performance */// 快速排序算法,将 sets 按照元素长度做排序,使最少元素的set排在最前面qsort(sets,setnum,sizeof(robj*),qsortCompareSetsByCardinality);/* The first thing we should output is the total number of elements...* since this is a multi-bulk write, but at this stage we don't know* the intersection set size, so we use a trick, append an empty object* to the output list and save the pointer to later modify it with the* right length */if (!dstkey) {replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c);} else {/* If we have a target key where to store the resulting set* create this key with an empty set inside */dstset = createIntsetObject();}/* Iterate all the elements of the first (smallest) set, and test* the element against all the other sets, if at least one set does* not include the element it is discarded */// 看来redis也是直接通过迭代的方式来完成交集功能// 迭代最少的set集合,依次查找后续的set集合,当遇到一个不存在的set时,上值被排除,否则是交集si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[0]);while((encoding = setTypeNext(si,&elesds,&intobj)) != -1) {for (j = 1; j < setnum; j++) {if (sets[j] == sets[0]) continue;// 以下是查找过程// 分 hash表查找 和 intset 编码查找if (encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {/* intset with intset is simple... and fast */// 两个集合都是 intset 编码,直接二分查找即可if (sets[j]->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET &&!intsetFind((intset*)sets[j]->ptr,intobj)){break;/* in order to compare an integer with an object we* have to use the generic function, creating an object* for this */} else if (sets[j]->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// 编码不一致,但元素可能相同// setTypeIsMember 复用前面的代码,直接查找即可elesds = sdsfromlonglong(intobj);if (!setTypeIsMember(sets[j],elesds)) {sdsfree(elesds);break;}sdsfree(elesds);}} else if (encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {if (!setTypeIsMember(sets[j],elesds)) {break;}}}/* Only take action when all sets contain the member */// 当迭代完所有集合,说明每个set中都存在该值,是交集(注意分析最后一个迭代)if (j == setnum) {// 不存储交集的情况下,直接响应元素值即可if (!dstkey) {if (encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT)addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,elesds,sdslen(elesds));elseaddReplyBulkLongLong(c,intobj);cardinality++;}// 要存储交集数据,将值存储到 dstset 中else {if (encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {elesds = sdsfromlonglong(intobj);setTypeAdd(dstset,elesds);sdsfree(elesds);} else {setTypeAdd(dstset,elesds);}}}}setTypeReleaseIterator(si);if (dstkey) {/* Store the resulting set into the target, if the intersection* is not an empty set. */// 存储集合之前会先把原来的数据删除,如果进行多次交集运算,dstKey 就相当于临时表咯int deleted = dbDelete(c->db,dstkey);if (setTypeSize(dstset) > 0) {dbAdd(c->db,dstkey,dstset);addReplyLongLong(c,setTypeSize(dstset));notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,"sinterstore",dstkey,c->db->id);} else {decrRefCount(dstset);addReply(c,shared.czero);if (deleted)notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",dstkey,c->db->id);}signalModifiedKey(c->db,dstkey);server.dirty++;} else {setDeferredMultiBulkLength(c,replylen,cardinality);}zfree(sets);}// compare 方法int qsortCompareSetsByCardinality(const void *s1, const void *s2) {return setTypeSize(*(robj**)s1)-setTypeSize(*(robj**)s2);}// 快排样例 sort.lua-- extracted from Programming Pearls, page 110function qsort(x,l,u,f)if l<u thenlocal m=math.random(u-(l-1))+l-1 -- choose a random pivot in range l..ux[l],x[m]=x[m],x[l] -- swap pivot to first positionlocal t=x[l] -- pivot valuem=llocal i=l+1while i<=u do-- invariant: x[l+1..m] < t <= x[m+1..i-1]if f(x[i],t) thenm=m+1x[m],x[i]=x[i],x[m] -- swap x[i] and x[m]endi=i+1endx[l],x[m]=x[m],x[l] -- swap pivot to a valid place-- x[l+1..m-1] < x[m] <= x[m+1..u]qsort(x,l,m-1,f)qsort(x,m+1,u,f)endend
sinter 看起来就是一个算法题嘛。
五、sdiffstore 差集处理
sinter交集是一算法题,那么sdiff差集应该也就是一道算法题而已。确认下:
// 用法: SDIFFSTORE destination key1 [key2]// t_set.cvoid sdiffstoreCommand(client *c) {// 看起来sdiff 与 sunion 共用了一段代码,为啥呢?// 想想 sql 中的 full join// c->argv[1] 是 dstKeysunionDiffGenericCommand(c,c->argv+2,c->argc-2,c->argv[1],SET_OP_DIFF);}// t_set.c, 差集并集运算void sunionDiffGenericCommand(client *c, robj **setkeys, int setnum,robj *dstkey, int op) {robj **sets = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*setnum);setTypeIterator *si;robj *dstset = NULL;sds ele;int j, cardinality = 0;int diff_algo = 1;// 同样的套路,先查找各key的实例// 不同的是,这里的key允许不存在,但不允许类型不一致for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {robj *setobj = dstkey ?lookupKeyWrite(c->db,setkeys[j]) :lookupKeyRead(c->db,setkeys[j]);if (!setobj) {sets[j] = NULL;continue;}if (checkType(c,setobj,OBJ_SET)) {zfree(sets);return;}sets[j] = setobj;}/* Select what DIFF algorithm to use.** Algorithm 1 is O(N*M) where N is the size of the element first set* and M the total number of sets.** Algorithm 2 is O(N) where N is the total number of elements in all* the sets.** We compute what is the best bet with the current input here. */// 针对差集运算,做算法优化if (op == SET_OP_DIFF && sets[0]) {long long algo_one_work = 0, algo_two_work = 0;for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {if (sets[j] == NULL) continue;algo_one_work += setTypeSize(sets[0]);algo_two_work += setTypeSize(sets[j]);}/* Algorithm 1 has better constant times and performs less operations* if there are elements in common. Give it some advantage. */algo_one_work /= 2;diff_algo = (algo_one_work <= algo_two_work) ? 1 : 2;if (diff_algo == 1 && setnum > 1) {/* With algorithm 1 it is better to order the sets to subtract* by decreasing size, so that we are more likely to find* duplicated elements ASAP. */qsort(sets+1,setnum-1,sizeof(robj*),qsortCompareSetsByRevCardinality);}}/* We need a temp set object to store our union. If the dstkey* is not NULL (that is, we are inside an SUNIONSTORE operation) then* this set object will be the resulting object to set into the target key*/dstset = createIntsetObject();if (op == SET_OP_UNION) {/* Union is trivial, just add every element of every set to the* temporary set. */for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {if (!sets[j]) continue; /* non existing keys are like empty sets */// 依次添加即可,对于 sunion 来说,有序是无意义的si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[j]);while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) cardinality++;sdsfree(ele);}setTypeReleaseIterator(si);}}// 使用算法1, 依次迭代最大元素else if (op == SET_OP_DIFF && sets[0] && diff_algo == 1) {/* DIFF Algorithm 1:** We perform the diff by iterating all the elements of the first set,* and only adding it to the target set if the element does not exist* into all the other sets.** This way we perform at max N*M operations, where N is the size of* the first set, and M the number of sets. */si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[0]);while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {for (j = 1; j < setnum; j++) {if (!sets[j]) continue; /* no key is an empty set. */if (sets[j] == sets[0]) break; /* same set! */// 只要有一个相同,就不算是差集??if (setTypeIsMember(sets[j],ele)) break;}// 这里的差集是所有set的值都不相同或者为空???尴尬了if (j == setnum) {/* There is no other set with this element. Add it. */setTypeAdd(dstset,ele);cardinality++;}sdsfree(ele);}setTypeReleaseIterator(si);}// 使用算法2,直接以第一个元素为基础,后续set做remove,最后剩下的就是差集else if (op == SET_OP_DIFF && sets[0] && diff_algo == 2) {/* DIFF Algorithm 2:** Add all the elements of the first set to the auxiliary set.* Then remove all the elements of all the next sets from it.** This is O(N) where N is the sum of all the elements in every* set. */for (j = 0; j < setnum; j++) {if (!sets[j]) continue; /* non existing keys are like empty sets */si = setTypeInitIterator(sets[j]);while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {if (j == 0) {if (setTypeAdd(dstset,ele)) cardinality++;} else {if (setTypeRemove(dstset,ele)) cardinality--;}sdsfree(ele);}setTypeReleaseIterator(si);/* Exit if result set is empty as any additional removal* of elements will have no effect. */if (cardinality == 0) break;}}/* Output the content of the resulting set, if not in STORE mode */if (!dstkey) {addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,cardinality);si = setTypeInitIterator(dstset);// 响应差集列表while((ele = setTypeNextObject(si)) != NULL) {addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,ele,sdslen(ele));sdsfree(ele);}setTypeReleaseIterator(si);decrRefCount(dstset);} else {/* If we have a target key where to store the resulting set* create this key with the result set inside */int deleted = dbDelete(c->db,dstkey);if (setTypeSize(dstset) > 0) {// 存储差集列表,响应差集个数dbAdd(c->db,dstkey,dstset);addReplyLongLong(c,setTypeSize(dstset));notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,op == SET_OP_UNION ? "sunionstore" : "sdiffstore",dstkey,c->db->id);} else {decrRefCount(dstset);addReply(c,shared.czero);if (deleted)notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",dstkey,c->db->id);}signalModifiedKey(c->db,dstkey);server.dirty++;}zfree(sets);}/* This is used by SDIFF and in this case we can receive NULL that should* be handled as empty sets. */int qsortCompareSetsByRevCardinality(const void *s1, const void *s2) {robj *o1 = *(robj**)s1, *o2 = *(robj**)s2;return (o2 ? setTypeSize(o2) : 0) - (o1 ? setTypeSize(o1) : 0);}
额,这个差集的定义好像过于简单了,以至于实现都不复杂。
六、spop 获取一个元素
前面讲的基本都是增、查,虽然不存在改,但是还是可以简单看一下删掉操作。spop有两个作用,一、获取1或n个元素,二、删除1或n个元素。
// 用法: SPOP key [count]// t_set.cvoid spopCommand(client *c) {robj *set, *ele, *aux;sds sdsele;int64_t llele;int encoding;if (c->argc == 3) {// 弹出指定数量的元素,略spopWithCountCommand(c);return;} else if (c->argc > 3) {addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr);return;}/* Make sure a key with the name inputted exists, and that it's type is* indeed a set */if ((set = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nullbulk)) == NULL ||checkType(c,set,OBJ_SET)) return;/* Get a random element from the set */// 1. 随机获取一个元素,这是 spop 的定义encoding = setTypeRandomElement(set,&sdsele,&llele);/* Remove the element from the set */// 2. 删除元素if (encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {ele = createStringObjectFromLongLong(llele);set->ptr = intsetRemove(set->ptr,llele,NULL);} else {ele = createStringObject(sdsele,sdslen(sdsele));setTypeRemove(set,ele->ptr);}notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_SET,"spop",c->argv[1],c->db->id);/* Replicate/AOF this command as an SREM operation */aux = createStringObject("SREM",4);rewriteClientCommandVector(c,3,aux,c->argv[1],ele);decrRefCount(aux);/* Add the element to the reply */addReplyBulk(c,ele);decrRefCount(ele);/* Delete the set if it's empty */if (setTypeSize(set) == 0) {dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del",c->argv[1],c->db->id);}/* Set has been modified */signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]);server.dirty++;}// 没啥好说的,就看下是如何随机的就好了// t_set.c, 随机获取一个元素,赋值给 sdsele|llele/* Return random element from a non empty set.* The returned element can be a int64_t value if the set is encoded* as an "intset" blob of integers, or an SDS string if the set* is a regular set.** The caller provides both pointers to be populated with the right* object. The return value of the function is the object->encoding* field of the object and is used by the caller to check if the* int64_t pointer or the redis object pointer was populated.** Note that both the sdsele and llele pointers should be passed and cannot* be NULL since the function will try to defensively populate the non* used field with values which are easy to trap if misused. */int setTypeRandomElement(robj *setobj, sds *sdsele, int64_t *llele) {if (setobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// 1.1. dict 型的随机dictEntry *de = dictGetRandomKey(setobj->ptr);*sdsele = dictGetKey(de);*llele = -123456789; /* Not needed. Defensive. */} else if (setobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {// 1.2. intset 型的随机*llele = intsetRandom(setobj->ptr);*sdsele = NULL; /* Not needed. Defensive. */} else {serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");}return setobj->encoding;}// 1.1. dict 型的随机/* Return a random entry from the hash table. Useful to* implement randomized algorithms */dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d){dictEntry *he, *orighe;unsigned int h;int listlen, listele;if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);// 基本原理就是一直接随机获取下标,直到有值if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {do {/* We are sure there are no elements in indexes from 0* to rehashidx-1 */// 获取随机下标,须保证在 两个hash表的范围内h = d->rehashidx + (random() % (d->ht[0].size +d->ht[1].size -d->rehashidx));he = (h >= d->ht[0].size) ? d->ht[1].table[h - d->ht[0].size] :d->ht[0].table[h];} while(he == NULL);} else {do {h = random() & d->ht[0].sizemask;he = d->ht[0].table[h];} while(he == NULL);}/* Now we found a non empty bucket, but it is a linked* list and we need to get a random element from the list.* The only sane way to do so is counting the elements and* select a random index. */listlen = 0;orighe = he;// 对于hash冲突情况,再随机一次while(he) {he = he->next;listlen++;}listele = random() % listlen;he = orighe;while(listele--) he = he->next;return he;}// 1.2. intset 型的随机// intset.c/* Return random member */int64_t intsetRandom(intset *is) {// 这个随机就简单了,直接获取随机下标,因为intset可以保证自身元素的完整性return _intsetGet(is,rand()%intrev32ifbe(is->length));}
OK, 至此,整个set数据结构的解析算是完整了。
总体来说,set和hash类型的实现方式还是有很多不同的。不过没啥大难度,就是几个算法题解罢了。

腾讯、阿里、滴滴后台面试题汇总总结 — (含答案)
面试:史上最全多线程面试题 !
最新阿里内推Java后端面试题
JVM难学?那是因为你没认真看完这篇文章

关注作者微信公众号 —《JAVA烂猪皮》
了解更多java后端架构知识以及最新面试宝典

看完本文记得给作者点赞+在看哦~~~大家的支持,是作者源源不断出文的动力
作者:等你归去来
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/yougewe/p/12247580.html
